AWS certified solution architect associate 🔗
Compute 🔗
EC2 Basic 🔗
EC2 Types: 🔗
- Generar purpose: A, T, M
- Compute: C
- Memory optimized: R, X, z
- Accelerated computing: P, G, F
- Storage Optimized: H, I, D
EC2 Purchase options 🔗
- on demand: pay per time of each instance (most expensive). Recommended for short term jobs that cannot be interrupted
- saving plans: lower prices but commitment to use X amount of USD per hour
- Reserved instances: lower prices but commitment to use a specific region, instance type
- Spot instance: bid for the time, good for analytics or short jobs that can be stopped
- Dedidacated hosts: Pay for a physical host, and bring your existing software licenses
- Dedicates instances: like on demand, but the physical host is not shared with anybody
- Capacity reservation: Reserve capacity for your EC2 in specific AZ for any duration (like reseverd instance, but in any time frame and apply and cancel in any time)
EC2 - Networking 🔗
- Security group: statefull (if you specify that a port is allowed for incomming, if a incoming request is started, we can talk back)
- NACL: Optional, rules at the level of subnet for allowing/denying trafic (stateless)
- Elastic IP: give a static ip to a EC2 instance, you can move this EIP around to give it to another instance (ie: fail mode, the instance doesn’t work and you give the IP to another EC2)
- Elastic Network interface: represents Virtual Network cards, this allows a EC2 instance to have more than 1 IP address in the subnet
EBS 🔗
EBS Volumes: Block level storage,
- performant (DB’s, system disks)
- flexible (can change size, IOPS etc.. on the fly, no longer need to stop instance to change size etc…)
- are not attached to EC2 lifecycle (we can store, paying, even if the EC2 is down)
- Can use Multi Attach (an EBS can be attached to multiple EC2 at the sametime)
- Only in io-1 and io-2 nodes
EBS types
- gp2, gp3 -> general purpose -> most recomended => 16K IOPS
- provisioned IOPS -> io1, io2 -> high performant => max 64k IOPS
- Throughtput optimized HDD (st1) -> low cost, high throughput, for frequent accessed data => 500 iOPS
- Cold HDD -> sc1 -> design for less frequently accessed workloads, the cheapest (even than st1) => for infrequent access => 250 ios
EBS Encryption
- at rest and at-transit, AES-256, use KMS
- Can encrypt the boot volumes as well
- all snapshots, and moving data is encrypted
EBS Snapshot
- Incremental, only the blocks that have been changed are backup
- Stored in S3
- Lazy Loading: Loads the blocks from S3 that are requests first
- if volume is encrypted, snapshot is encrypted
EBS RAID
- Raid 0 -> 2 volumes as 2. Gives I/O performance. Lost of a single volume you lost all the data
- Raid 1 -> 2 volumes as 1. gives fault tolerance
- Not use for root volumes
Best Practices 🔗
- Securiy
- use System manager to not have to open port 22 to the EC2 machine
- Regularly patch update and secure the OS and software (IAM)
- Storage
- use separate EBS for the OS and the Data
- Ensure volume persist after instance termination
- use instance store for temporary data (the instance story is not persisted)
- on stop will be deleted
- cannot add instance stores once the EC2 instance has started
- Regularly backup your EBS volumes using EBS snapshots
Elastic IP 🔗
- Public ip that can be associated to an EC2
- EIP is static (doesn’t change) (contrary to the public IP that all EC2 gets)
- is charged only while is associated with an active instance
- not supported for IP6
AMI 🔗
Defines the information needed to launch an instance, you can launch multiple instances with a single AMI. Consist of:
- One or more EBS snapshots, or instance store (the data is temporal)
- Launch permissions (to control which accounts can use the AMI)
- a block device mapping (that EBS goes to this mount folder)
You can copy AMI to another region
Hibernate EC2 Linux instance 🔗
- When stopping the EC2 instance the memory is dumped into the EBS
- EBS is persisted
- When the instance is resumed
- Recover the EBS to the last state
- RAM is reloaded
- Rerun all the previous processes
- Data volumes are reattached and the instance keeps it’s instance id
Requesites:
- instance type should be C, I, M, R, T
- less than 150Gb
- The AMI should support hibernate (Linux2 AMI or ubuntu AMI. Also there is a process to make a custom AMI compatible)
- Should use an EBS gp2,gp3 or io1,io2
- Root volume must be encrypted
- Hibernation should be enabled at launch
Limitations:
- You loose data on any instace store values
- Cannot change the type and size of an instance that has hibernation enabled
- cannot hibernate more than 60 days
- cannot hibernate an instance in an ASG or used by ECS
- If an instance is hibernation, will not be hot patched (you need to start hibernate again)
ELB (Elastic Load Balancer) 🔗
Types:
- Application Load Balancer (ALB)
- Network Load Balancer
- Gateway Load Balancer (IP)
- Classic Load Balancer
Cross-Zone Load Balancing: When the ELB routes request to services in another AZ. Enabled by default in ALB, and disable for Network Load balancer
Sticky Sessions 🔗
- Cookie sessions, handled directly by the ALB
- Cookies allow to always use the same target in a target group
- if the target is no longer available, it routes to a new target and changes the cookie
- cooki is encrypted
ASG Auto Scaling groups 🔗
- High Availability: Maintains compute capacity for optimum performance
- Fault Tolerance: Replaces unhealtht instances for healthy ones
- Cost Savings: Adjust compute capacity to the current scenario
- Free (You pay for the instances)
Termination policies: determine which EC2 instance to be terminated first
- allocation strategy
- oldestLaunchTemplate => useful to make sure most instances has the newest IAM
- OlderLaunchConfiguration
- ClosesToNextInstanceHour => “save” money
- OldestInstance
- Newest Instance
How it works 🔗
Launch configuration 🔗
Is a template to replicate the instance (AMI, UserData, Storage, Security Groups, Instance Type, Key Pair etc…)
Auto Scaling Group 🔗
- Logical aggroupation of instances in the ASG
- Scales the compute capacity (creates/destroys) instances
- Does the periodic Health Checks. Terminates instances in bad shape
- Minimum, Desirec and Maximum capacity
- There are Scaling policy that adjust the desired capacity.
Scaling options 🔗
- Maintain current instance all time
- Manual scaling
- Scale based on schedule
- Scale based on demand (ie. CPU)
- an ASG can have more than 1 scaling policy
Rules to decide what to terminate in an ASG 🔗
Instances with oldest Launch Config -> Closes next billing hour -> Random
ASG Lifecycle Hooks 🔗
There are hooks between each ASG instance state, we can hook for 1 hour into them. Max of 50 hooks per ASG
- Pending:Wait (new instance)=> install software
- Terminate:Wait (destroying instance)
Limits: MAx time you can be in a wait state is 48hour or 100 time the heartbeaat
ASG Cooldown periods 🔗
There is a cooldown to the scaling policies, to make sure new instances have time to impact the metrics.
default cooldown period is 5min
AWS Lambda 🔗
Limitations:
- Max memory 10Gb
- Max time 900 seconds
Lambda Edge 🔗
- Is to have compute at cloudfront edge (closer to the user)
- Supports nodejs and python
SAM Serverless Application Model 🔗
Two components
- SAM Template specification
- SAM CLI
Is like a opensource language of the cloudformation for Serverless services (Lambda, dynamodb)
Is a simple syntax
Storage 🔗
S3 🔗
Is an Object stored (as oposite to Block Storage like EBS)
Concepts:
- Bucket
- Object -> global
- Key
in S3 bucket you can chose the region to optimize latency or regulatory requirements. They never leaves the region if you don’t say so.
S3 is redundant in 3 AZ automatically.
S3 consistency: have a strong read-after-write consistency. if you write and read at the same time, you will read the old/new version. but never partial or corrupted data
Locks 🔗
- Retention locks => denies to modify or delete an object for a period of time
- Legal locks => denies for ever to modify or delete an object
Versioning 🔗
- Price
- You can not unversion a bucket that is already versioned (you from unversioned to versioned, and from versioned to suspended versioned)
- On delete of a object it just hides the data with a Delete Marker
- You can delete the object with a version id, but instead it permantely delete
- You might seem 503 slow down, if the app is updating to many version in a versioned bucket
MFA 🔗
We can add MFA to bucket, to make sure that updates and deletes are need to have a second authentication.
Server and Object LEvel Access Logging 🔗
- S3 have the ability to log all the access done to S3 objects for compliance
- S3 Server access logging
- Best Effort bases (some logs can be lost)
- GET/PUT/POST/OPTIONS, IP, AWS account, BUCKET, data size
- upload to an S3 log bucket
- Some operations are not logged (like bucket listening, creation or deletion of buckets)
- S3 object level logging
- use cloud trail events to get information of the bucket and the objects
- You need to creat a cloud trail manually
- all events can be logged -> if the bucket is very busy could lead to performance issues / costs
- S3 Server access logging
Static websitte 🔗
- amplify allow you to have SPA hosted (amplify has more services apart of hosting, like auth, graphql etc…)
- doesn’t support HTTPS (you need put cloudfront)
- errors will give you html instead of XML error for Rest API
Encryption 🔗
- at rest
- Server side encryption
- SSE-S3
- Is the most managed option
- Object are encrypted with a unique key (generated by S3), the key is encrypted with a master key that is regularly rotated
- To force the whole bucket to be encrypted, you need to add a bucket-policy that denies permission to upload the object unless there is the x-amz-server-side-encrypted header
- SSE-KMS
- Similar to SSE-S3
- the key is managed by KMS -> meaning you have more granual control of who is using this key, and more auditory
- The S3 request the unique-key to KMS
- SSE-C (Customer provided keys)
- You manage the encryption keys
- S3 encrypts and decypts the data but does not store the key
- It stored a randomly salted HMAC of the encryption key to validate future requests
- if you lose the encryption key, you lose the object
- SSE-S3
- Client side encryption
- Client side encryption with KMS -> before sending the object, we ask for a key, S3 library encrypts the data, and then we upload to S3
- Server side encryption
- in-transit
- SSL/TLS
Transfer accelaration 🔗
Bucket level featur for sending data fast to any bucket over long distances
- The client send the data to the cloudfront edge locations
- Cloudfront send to the proper S3 region using and optimized network path
- Needs to be enabled at bucket level
Multipart upload 🔗
Split file in multiple parts, and send it to S3 in parallel. Recommended to use once we have object around 100M
S3 Events 🔗
When an action (new, remove, restore) is uploaded we can publish events, so other systems can detect and do somethings
can publish events to SNS (no fifo), SQS (no fifo), Lambda
to allow to S3 events to publish the eventwe need to grant the S3 principal permission to call the API (SNS, SQS or lambda)
Requester Pays 🔗
in S3 the owner of the buckets you pay for storage, request and download.
With Requester pays, the owner of the bucket only pays for the storage
Permissions 🔗
Access Control List (ACL) 🔗
Which AWS accounts or groups are granted access and the access type
To give permissions (READ/WRITE) to other AWS accounts. Is the only way to manage access to the object not owned by the bucket owner
Bucket Policy 🔗
Grants other AWS accounts or IAM user access ppermission for the bucket and the objects in it
You should use buccket policy when you want to manage cross-account permissions
Object Lifecycle 🔗
Move objects to different storage classes (depending how much they are used) or expiration
You cannot transfer the objects to another storage class before 30 days. You can use different policies for different versions of the same object
Cross Region Replication CRR 🔗
Automatic async copying of objects from a bucket in one region to another bucket in another region
Versioning has to be enabled
if objects are encrypted with SSE-S3 or SS3-KMS the copy is also encrypted
the metadata (tags, etc) also is copied
Not replicated if….
- Objects added before the replication was enabled
- SSE-C encrypted objects
- Objects that are replicas from anothes Cross-Region Replication are not replicated
- Deletes of a specific version are not replicated (deletes of a general version, the delete marker are replicated
- )
Method + domain (ie: allow GET+POST from somedomain.com)
Pre-Signed URLS 🔗
Grants a user temporary access to a S3 object
- the credentials are those who generated the Pre-Signed url
- You can list buckets or get_bucket_location
S3 Storage Classes 🔗
Storage class is defined at object level
- S3 Standard -> General purpose storage frequently accessed data (low latency and high thoughput)
- S3 Standard-Infrequent Access (IA) -> Long lived but less frequently accessed data
- Cost less, but charges you for retrieving Data
- need the data to be at least 30 days
- S3 One Zone-Infrequent Access (IA) -> Like the S3 IA but only in un AZ
- S3 Intellinget Tiering -> Cost optimization without performance impact
- S3 Glacier (Flexible retrieval) and S3 Glacier Deep Archive -> Long term storage
- Deep Archive -> data retrieve can take 12 hours . 48h
- Flexible retrival =>
- Expedite 1-5 minutes
- Standard => 3-5 hours
- Bulk => 5-12 hours
- S3 Glaclier Instant Retrieval => milliseconds access time, rarelly accessed data (once a quarter)
- You can buy provisioned retrieval capacity => 3 expedite each 5 min
Select From 🔗
Query CSV/Parquet etc… files directly in SQL
Glacier Vault 🔗
Can have a:
- Valut access policy -> to manage access permissions to the vault
- Vault lock policy -> to “lock” the policy and no change can be made to the policy
EFS Elastic Filesystem 🔗
- Storage capacity is elastic
- Supports NFSv4
- Multiple instance can access at the same time
- Can enable encryption at-rest and in transit
- Performance modes
- General purpose
- MAX I/O
- Single region, replication in multiple AZ
Can have different storage class
- Standard
- One Zone
- Standard Infrequent access
- EFS One Zone IA
Storage Gateway 🔗
Connects a softwate applicace (phisical!) from your datacenter with cloud based storage seamlessly.
Thre options
- File based -> File Gateway a VM that does (NFS/SMB) -> to S3
- S3 File Gateway =>NFS/SMB
- FSx File Gateway (only SMB)
- Volume based -> iSCSI -> Volume Gateway -> to S3
- Cached volumes (only the most used data in S3 is keep in the gateway)
- Stored volumes (the whole volume is keep in the gateway)
FSx 🔗
Fully managed MS windows file system (SMB protocol)
You can use MS Active directory
Lustre FS 🔗
_Lustre_® file system is an open-source, parallel file system that supports many requirements of leadership class HPC
- scratch => temporary storage, short-term data processing => is not replicated and doesn’t persist
- Persistent => longer term storage, is replicated in multiple AZ
AWS Parallel Cluster 🔗
self service cluster management tool
Snowball 🔗
petabyte scale data prouct transport solution to transfer large amount of data
They send you a device, you store the data in the device locally (with keys and every thing is secure). and send that to them and appear to S3
Snowball Edge 🔗
Is a data transfer device having onboard storage and compute capabilities, supports data processing with AWS compute like Lambda
Security 🔗
IAM (Identity and Access management) 🔗
IAM is a service that enable to manage access to AWS services and resources securely
Concepts:
- Resources
- IAM users
- IAM groups
- IAM Roles (not need authentication, because they are already AWS resources)
- IAM Permissions
- IAM Policy (JSON)
- IAM Principal (User, Role, Federated User or Application) can be permanent or temporal)
You attach multiple policies to each User/Group or Role
IAM Policies 🔗
Flow of policies
- a Principal makes a request to AWS
- First check that the user is authenticated (logged or with valid credentials)
- Second check if they are authorize to make the request -> here is where the policies apply
- Most policies are Identity based (Users or Role) or Resource based (depending where you attach them). I can attach a policy to a user that they can use a bucket, I can attach a policy to the bucket saying the user X can use this bucket
- IAM checks all the policies that apply to the request
- If a single one denies, then the request is denied
- If there is no policy the request is denied as well (except root users)
For a request in a different account, a policy in the target account must allow access to the resource,and the source IAM entity must have an identity based policy that allows the request -> will not be visible in the console
Types of policies 🔗
- Identity based policies
- Managed policies (they could be AWS managed or custom managed)
- AWS managed policies like -> you can access the whole S3
- Inline policies
- Managed policies (they could be AWS managed or custom managed)
- Resource based policies -> attached to the resource, and says which principal (User/Role) can access (from the same account or from other accounts)
- permission boundaries -> this are rules that limit the max that an identy-based policy can grant to a role
- Organization SCPs (Organization Service Control Policy)
- Access Control Lists
- Session policies
IAM Roles 🔗
- a role is something a user can tap into, to have extended rights
- There is a Trust policy which defines which principals can be associated with the roles
- and the policy (permissions) that the role grant
- You can use this for users or for servers
Best practices 🔗
- Look away your AWS root user and access keys
- Create individual IAM users
- Strong password policy
- Rotate credentials regularly
- enable MFA
- prefer use groups to IAM users
- Use AWS definied policies
- Grant least privilege
KMS 🔗
Managed service that makes it easy to create and control encryption keys
- Integrated with most other AWS services
- Creates and securely stores your master keys called CMKs FIPS 140-2
- You can use AWS cloudHSM clusters
- KMS keys are region specific, but AWS is introducing multi region keys
- CMK => don’t support digital signature verification
Cloud HSM 🔗
Store and managed keys and encrypt on your actual data
is a hardware security module, you can deploy into your own VPC
- comply with FIPS 14002 level 3
SAML Federation 🔗
Just use users from other Authentication directory that uses SAML (a lot of identity providers) without needing a IAM user in AWS
You can use Active Derectory Federation Service -> the same but using active directory
Active directory 🔗
- AWS Directory service for Microsoft AD -> Managed AWS Active Directory
- AD Connector
- Proxy service that connects some AWS Applications and Windows Server EC2 instance to on premise MS AD
- Simple AD: A clone MS AD with less features
- Cognito user pools: a service that allow user to login with SAML to webapps or mobile apps
WAF (Web application firewall) 🔗
Monitor trafic HTTP requests
in front of CloudFront/Load BNalancer/ ApiGateway
can add rules with (WebACL):
- Cross Site Scripting
- IP address
- Country or geo location
- Length of specified parts of the request
- SQL Injectio
Can add rate based rules to
- blanked rate based rule: a single IP does too many requests
- URI specific rate based rule: a single IP does too many request to a single URI
- IP Reputation rate based rule: prevent well-known malicious IP addresses
Shield 🔗
Provides protection agains DDoS attacks
- AWS Shield standard: free and enabled
- AWS Shield advance: expanded DDoS attack protection
Security Hub 🔗
AWS Security Hub is a cloud security posture management service that performs security best practice checks, aggregates alerts, and enables automated remediation.
AWS Resource Access Manager 🔗
securely share AWS resources across AWS accounts
You can use a resource (a RDS or whatever) to multiple accounts
You specify the resource to share, the operations that can be done in the resource, and who can use the resource (roles/users)
- resources are visible into the console (instead if we do a IAM cross-account)
Security Token Service STS 🔗
Enables to request temporary, limited-privilege credentials for AWS IAM users
This gives permissions in AWS for example for users that log with SSO/SAML
This is what allow you to AssumeRole or AssumeRowWithSAML-> that give you temporary keys
Cognito 🔗
Provides authentication, authorization and user management for web and mobile apps
Components
- User pools -> User directory (sign-up/sign-in)
- Identity Pools-> grant users to other AWS services temporary
- Cognito sync -> sync user data and profile between different devices
Secrets Manager 🔗
Replace hard coded credentials in your code
- You can rotate the secrets, with a scheduled lambda
- uses KMS to encrypt the secrets
- there are version of your secrets
Guard duty 🔗
A service that monitors VPC Flow logs, Cloud Trail event log, Cloud trail S3 data and DNS Logs to detect threat
- Uses ML and intelligence feeds (as IP address and domain)
- exposed credentials
- EC2 mining bitcoin
- monitors AWS account access behavior
Amazon inspector 🔗
Test network accessibility of EC2 and security state of applications running on thos instances
- Can assess exposure, vulnerabilities and deviation from best practices
- Has an agent of EC2 instances being assessed
Macie 🔗
Fully managed data security and data privacy service that uses ML and pattern matching to help discover, monitor and protect sensite data in AWS
- Can discover PII and financial data stored in S3
- Identify report buckets that have excess permission
- You can create custom data identifiers
Databases 🔗
RDS 🔗
A relational Database
- Storage is the same as the EC (Magnetic, General purpose (SSD), and IO)
- RPO (Recovery point objective) -> is the maximum period of data loss acceptable in the event of failure or incident
- RTO (Recovery time objective) -> the maxium period of time permitted to recover from backup and to resume processing
Parallel query 🔗
IS a feture in aurora for MySQL that makes it possible to perform analytical queries over the data stored, without copying the data to a separate system
RDS Proxy 🔗
Feature in RDS which controls the connection pools, reuse them etc…
Backup 🔗
-> Backups can be done in a backup window -> backups are incremental (first is full, next are incremental) -> You can copy manual and automatic snapshot, but can only share manual snapshots
Transparency Data encryption 🔗
- Suported by Oracle, SQL Server.
- Data is encrypted before it’s written and decrypted when data is read fro mthe storage
- ORacle => can be integrated with CloudHSM
Multi AZ - HA 🔗
We can have a Multi-AZ (slave-master) that replicates (sync Replication) to another AZ, and when the first one is down, the dns name change and points to the second one -> during updates, the slave becomes the master
Read Replica - High scalability (Horizontal) 🔗
- it can be in another AZ , even in another region (if you enable cross region)
- You can make apps that only read to use a Read replica
- Might not be updated 100% (there is a lag) (Async replication)
- You can create a read replica from a read replica -> but this could increase the lag
- all the databases will be replicated (you can not select which database to replicate)
- it can be promoted to a new normal RDS instance -> could be used as HA -> but is manual
IAM DB Authentication 🔗
-> instead of credentials you login with just the IAM - Trafic is encrypted usign SSL - only mysql + pgsql
DynamoDB 🔗
Fully managed, multi-region, multi-master NoSQL database service with low latency and seamless scalability
- Tables -> a collection of data -> contains 0 or more items
- Items -> A group of attributes that is uniquely identifiable among all of the other items. Is composed by one or more attributes
- Attributes -> a fundamental data element
- Primary key -> identifies an item in the table -> two items can not have the same PK
- can be composed or a single attribute
- composed (a partition key + a sort key)
- PK is used to partition the table
- Secondary indexes (5 max GSI and LSI)
- You need index to make certain queries if you don’t want to do a full scan
- Global Secondary index -> The index has not the same items as the PK, so the items can be in any partition
- Eventual consistency only
- Local Secondary Index -> the index has the same items as the PK, but different sort keys -> which means the items in this index are in the same partition as the PK
- You cannot create LSI after the table creation
- Both eventual consistency or strong consistency
Read Consistency 🔗
DynamodDB supports two types of consistency:
- Eventual consistent Read
- If you read after an update, it might not be reflected yet
- Strong consistent Read
Read/Write Capacity 🔗
When you configure a new table, you must define the Read/Write capacity
- Read Capacity Unit => 1 Strong consistent read or 2 eventually consistent reads per second for up to 4kb in size
- Write Capacity Unit => 1 write per second for an item up to 1Kb in size
If your read/write requests exceed the capacity, DynamoDB can throttle the request from consuming too many capacity units with a 400 code / ProvisionedThrougputExceededException
Autoscaling 🔗
Adjust provisioned throughput capacity on your behalf
- Need a DynamoDB AutoScaling Service Linked Role (IAM)
Encryption 🔗
Encryption at rest
- You cannot enable after the creation of the table, and cannot be disabled
- AES-256
- can be
- fully AWS managed
- or you can choose KMS key (Pay for it)
Query vs Scan 🔗
Query 🔗
- Finds items based on primary key values
- You must provide the name of the partition key attribute, and a single value for that attribute
Scan 🔗
- always scans the entire table or secondary index
DynamoDB Accelarator (DAX) 🔗
Cache for DynamoDB, microseconds
- Can evitate the Read/write througput
Streams 🔗
Captures data modification events in the same order of ocurrence
What is in the stream
- New item
- Update -> (we have before and after)
- Delete item
=> Delivers only once => 24h of retention
AWS Lake Formation 🔗
to setup Data lakes in days, permissions to columns, row and cell levels, storage into S3
Global tables 🔗
provide a fully managed solution for deploying a multi-region, multi-active database without having to build and maintain your own replicat solution
Neptune 🔗
Graph database
Aurora Endpoint 🔗
- Cluster endpoints => connects to the primary db instance of the db cluster
- Reader endpoint => load balance between all the read replicas in the cluster
- instance endpoints => points to specific db instance in the cluster
- custom endpoint => connects to user-defined db instance of the cluster
Aurora Serverless (v1) 🔗
like an RDS where the database compute can autoscale (even sleep) if there is no consumption, decopling compute from storage
- Fault tolerant -> 6 copies across 3 AZ
- You define ACU (Aurora capacity units)
- 1 ACU is 2Gb of memory, corresponding CPU and networking
- You define the max and min of ACU’s
- also the storage scales from 10Gb to 128Tb
Limitations:
- Some regions
- Aurora MySQL and Aurora Postgresql
- and more…
Aurora Global 🔗
is like a Cross-region RDS of aurora, you have 2 instances, one in one region, and the other in another region (or multiple other regions), the first is the primary and the secondary has async replication
- the replication is much faster than Multi-AZ RDS
- you can change which region is the primary (less of a minute)
- is similar to Read Replicas, but you can change the primary in no time
Elastic Cache 🔗
Memory cache for low latency access
- Support Memcache, Redis
- Memcache
- prefered => when asking for K/V (like session)
- No has MultiAZ
- redis
- Has MultiAZ
- Memcache
- Managed by Amazon
Security 🔗
- encryption at-rest and in transit
Scenarios
- Same EC2 is in the same VPC as ElasticCache
- create custom rules in the securityu group for redis that allow connections from the security group of the EC2 instances
- EC2 and Elastic cache, same region but different VPC
- You need a VPC peering, make sure the VPC ip’s dont overlap
- Different VPC and different region
- Create a transit VPC
Session store 🔗
ELB stickysessions, when the EC2 ends (ASG or update) users will lose the session and start again
if we store it in ElastiCache Redis. we don’t lose session
App Sync 🔗
managed graphql service to interact with data source services (lambda, dynamodb)
You can query multiple databases, microservices and APIS with a single graphql endpoint
- USes caching to improve performance, subscription for realtime, and sync offline clients.
- Automatically scales depending on the API request volume
Management and Governance 🔗
Organizations 🔗
OU => Organization Unit => you build a tree of accounts
- Tag policy => forces accounts to all the resources to have specific tags (Owner, cost center etc…)
- Service Control policy => you can control what accounts can request (method) on services in AWS
- They don’t have any effect into the management accounts, only to the members accounts
Consolidated billing => get one bill for all the accounts + since it has all the usage, you might get better price
Monitoring 🔗
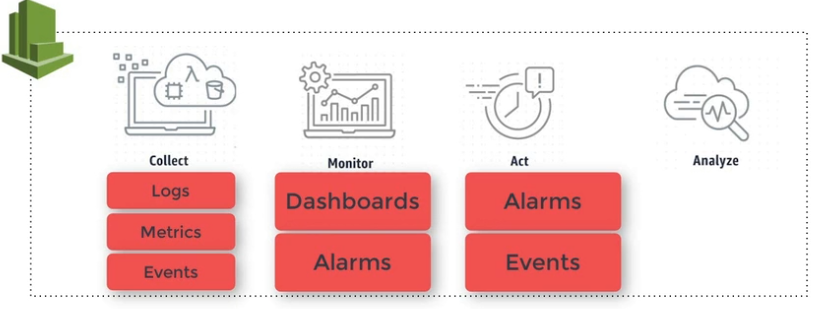
- You can have detailed monitor (to pass from 5 min period to 1 min period) => paying of course…
- Metrics -> default vs custom (memory is custom)
CloudWatch 🔗
-> can be streamed to kinesis directly, in real time -> Can capture AWS API calls
AWS System Manager 🔗
View and control AWS infrastructure. See the status of your compliance, security etc…
- Most EC2 instances have the system manager agent installed
CloudFormation 🔗
- I didn’t go over…
Concepts 🔗
- Output => Resources managed you can import into another stack
- Mappings => set values, depending on some inputs (AMI’s from region code)
- Parameters => input parameters to your teample each time you create/update
- Conditions
Hooks 🔗
cfn-hup => checks any update on the metadata, if there are any changes execute the hook
cfn-signal => can be used to signal CloudFormation to indicate if software or applications has been succesfully updated on an EC2 instance
cfn-get-metadata: helps to retrieve metadata for a resource to a specific key
cfn-init: retrieve and interepret resource metadata
- Fetch and parse metadata from CF
- install packages
- write files to disk
- enable/disable/start/stop services
Custom resources can be created from
- lambda function => will be executed, and you can change the template
- SNS =>a notification is done, some compute and will notify back Cloudformation to continue the deploy of the stack
Cloud Trail 🔗
Enables governance compliance and operational and risk auditing
Records events happening in AWS account (Conse, CLI or API)
- 90 days of retention => can be stored in S3 to more days
- can be processed as stream in kinesis
- Not 100% realtime (5 / 10 minutes)
CloudTrail Lake 🔗
Organization can easily capture & maintain AWS resource changes for 2 years, Being managed, has built in mechanisms for ensuring security and integrity of the datafiles
OpsWorks 🔗
Puppet and Chef
SMS System Manager Session 🔗
allow to SSH to EC2 instance without SSH, need the SystemManager role
System Manager Run Command 🔗
Same as System Manager Session, but you can ask to run a command to multiple EC2 instances
SSM (System manaer parameter Store) 🔗
Stores parameters (configuration) hierarchical and secret management
- can store clear and encrypted data
- Does not implement password rotation lifecycle (like the SecretsManager)
Encryption =>
- Standard parameters:
- encrypted and decrypted using the suplied CMK (KMS)
- Advanced parameters
- use Envelope encrypted with AWS Encryption SDK to encrypt/decrypt
- You can convert standard into advanced, but not the other way around
Trusted advisor 🔗
Looks at your account, and give you advise for best practices to save money or improve performance and reliability and security
AWS Well-Architected framework 🔗
a tool to understand the pros and cons of decisions while building system on AWS
Pilars: Reliable, Secure, Efficient, Oprationally excellent and cost-effective
Networking 🔗
VPC 🔗
It’s a private network that you define on AWS, you define your network as you would do in premise
Concepts:
- Region: a VPC belongs to a single region, but you can have more than one VPC in a region, can span multiple AZ though
- CIDR: 10.0.0.0/16 primary CIDR block -> it’s a way to define blocks of IP’s
- Subnet: Is a part of a VPC, with a CIDR, a subnet cannot span multiple AZ
- typically you would create 2 subnets for each AZ (one private and another public)
- NAT: a bridge between the network and the public internet, It’s a EC2 instance. You put it into the public subnet.
- So the private subnet can route to this NAT and then to the internet, but the connection can not be started from interinet
- NAT Gateway: Managed NAT by AWS, the NAT instance you can constumize it (and fuck it up). There is redundancy in Gateway.
- Public => instances in the private subnet can access the internet
- Private => instance in the private subnet can access other VPC or the data-center
- Internet Gateway (IGW): that actually the service that is connected to the internet. Provides routes to internet and performs NAT for instances that have public IP address.
- Difference between NAT gateway and IGW
- NAT work at the subnet level, and IGW at the VPC level
- Route Table: Rules that determine where network trafic is directed (CIDR -> target). When we add a NAT or a IGW, we should update the route table. There is a default route table created with the VPC
- Security Groups: Determines what traffic can go in/out of an instance. Stateful if the incoming trafic is allowed, the outgoing is allowed as well.
- NACL:
- Subnet level
- You define rules to allow/deny traffic
- Stateless => you need to define inbound and outbound rules
- by default they allow all the traffic in and out
- Rules: Rule number, Protocol, Source CIDR + port, Destination + port, allow or deny
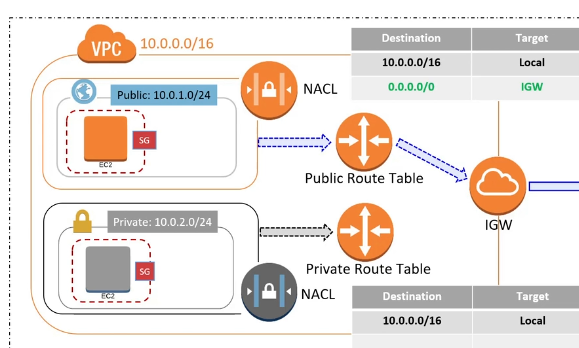
VPC Peering 🔗
VPC peering connection, allow to connect two VPC’s networking, and allow route traffic between them using private IPv4 or IPv6
- Can be between accounts, regions
- No single point of failure cause you are not deploying an instance, you are reusing VPC infrastructure
- You CANNOT edit VPC peering connection once is created, attach or detach
- Basically allow you to modify the route table, to say the ip-addres of the other VPC are available thorug the VPC peering
- Cannot be used if the CIDR overlap
- is not transient
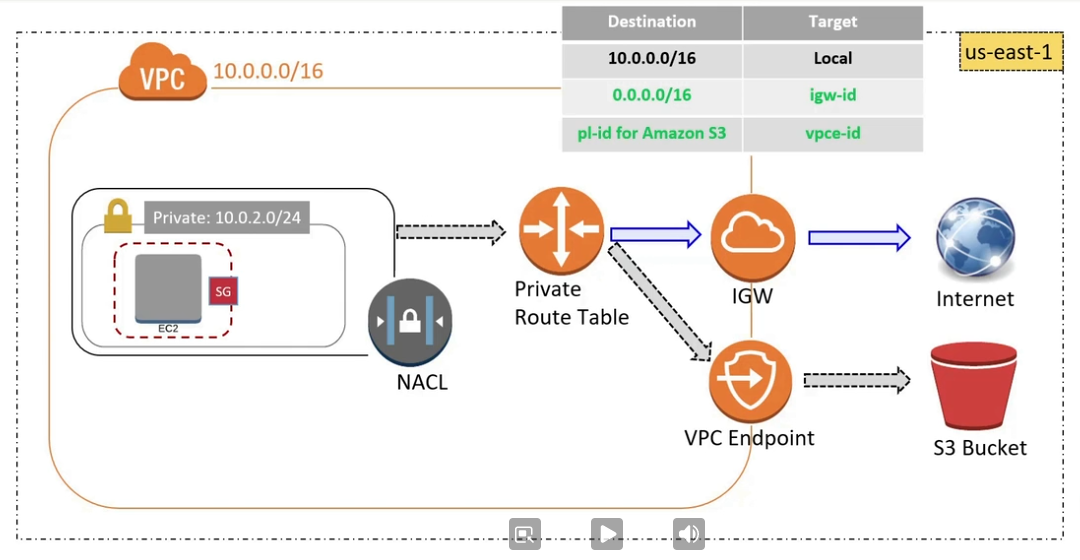
VPC Endpoint 🔗
Virtual device that enable to connect to supported AWS services and VPC endpoint powered by privateLink without any IGW, Nat, VPC or AWS Direct Connect. Without never leaving the Amazon network
VPC Flow Log 🔗
Gather information about the IP traffic going in and out of the VPC
Can be published to a CloudWatch or S3 Bucket
Private Link 🔗
It allow to create VPC endpoints, so others can route trafic to our services without hitting the internet.
You create a Gateway Load balancer endpoint, to allow trafic to come to the other vpc
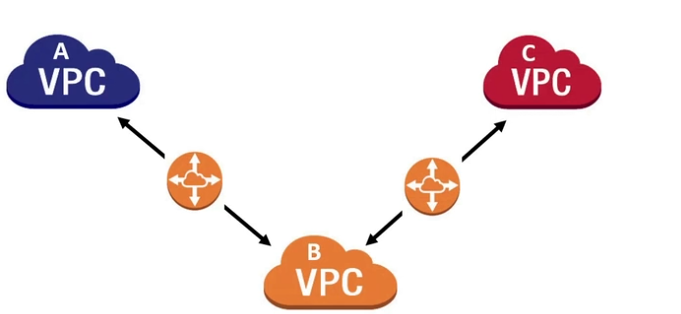
Transit Gateway 🔗
allow to interconnect multiple VPC and on-premises networks, and elastically scales
can interconnect:
- One or more VPC
- connect SD-WAN/third-party network applience
- AWS Direct Connect gateway
- a peering connection to another transit gateway
- a VPN connection to a transit gateway
AWS VPN 🔗
allow connect on premise network to the VPC\
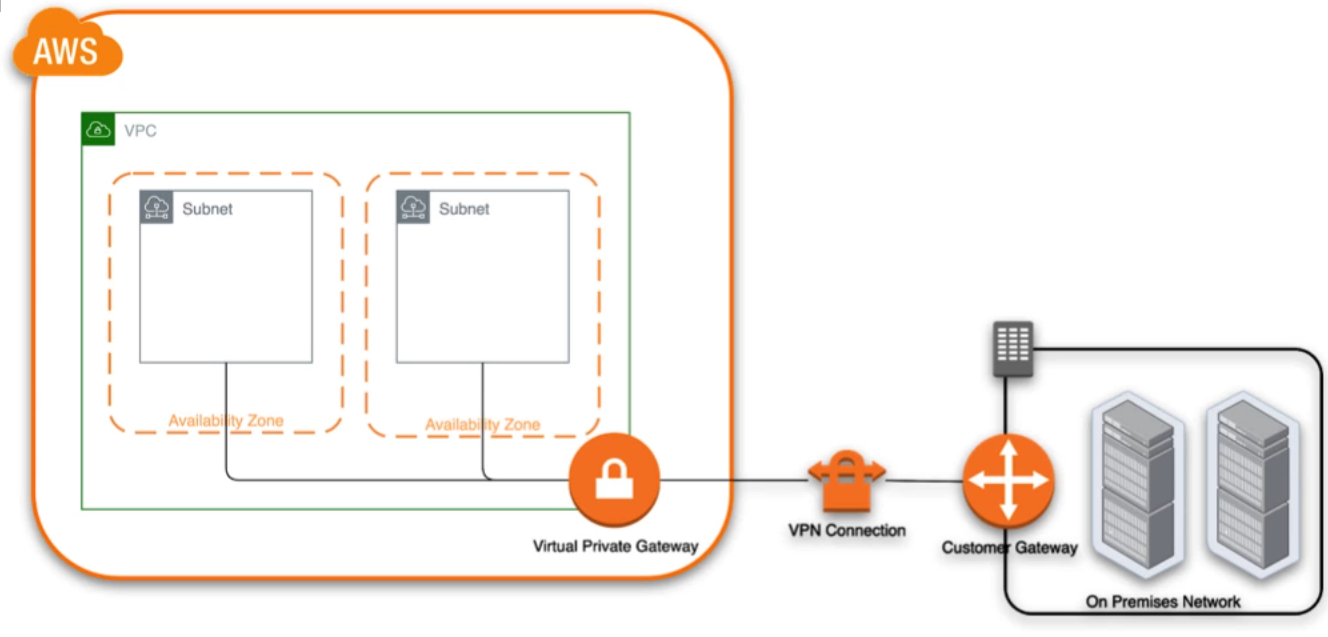
You need to setup a Customer Gateway into the on premise infra. you could connect to a traffic gateway
Limitations:
- No IPV6
- Overlapping CIDR blocks
AWS dirrect connect 🔗
Provides a dedicated connection from an on-premise network to a VPC
You actually connect a physic device to the router of the datacenter, so you can connect without going through the ISP.
To use it, you need to be in one of the AWS Direct Connect locations.
- 1Gb or 10Gb dedicated network connection
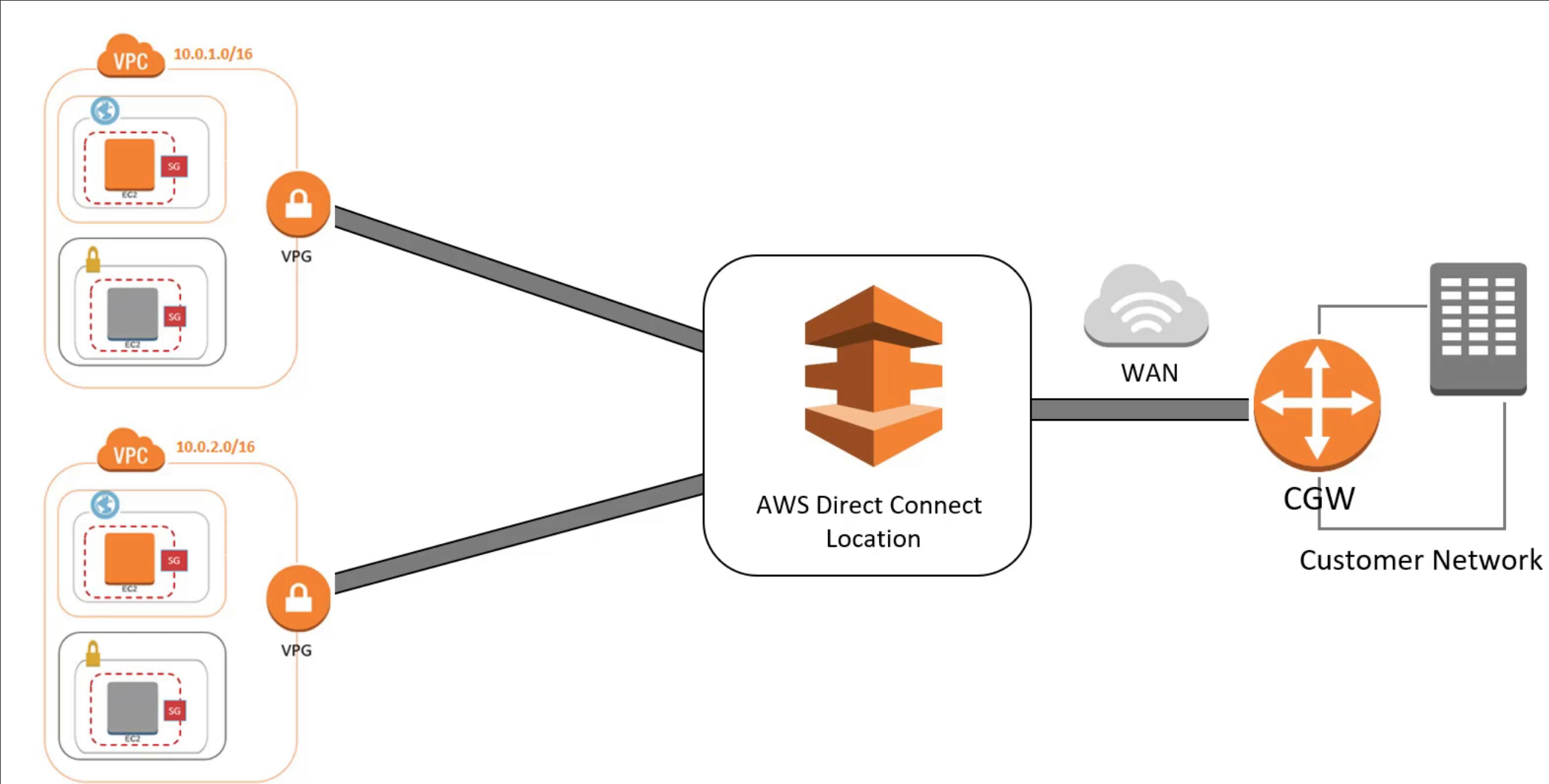
AWS Global Accelerator 🔗
Uses the AWS global network, to optimize the path from the users to your application.
You normally setup with different ALB’s in different regions, behind the AWS Global accelerator.
provides two anycast static IP addresses
Better for non HTTP applications
AWS API Gateway 🔗
managed service to create, publish, maintain, monitor secure your own rest and websocket APIS
Does things like accepting connection, monitor, authorizations, version management
- specially useful for lambdas
Features
- API Caching => so the API gateway caches and sent less requests to the backend nodes
- Gateway Response customization in OpenAPI => useful to customize error responses sent by the Gateway
- Response model => setup response format
- Mapping templates, to transform the request from the API to the backend nodes, or the response from the backend to the frontend. in Velocity template language
ENI, ENA, EFA (Network interface card options diff) 🔗
ENI (Elastic network interface) 🔗
- the most basic of the 3, is a virtual network card
- HAs a
- Primary IPv4 in your VPC
- can have more secondary IPv4
- One EIP per private IPv4
- One public IPv4
- multiple IPv6
ENA (Elastic network adapter) 🔗
- uses a single root I/O to provide high performance network capabilities => less latency
- 100Gbps
- or Intel VF of 10Gbs
EFA (Elastic Fabric adapter) 🔗
- Accelerates High performance computing and machine learning aplications
Cloud front 🔗
CDN service of AWS (Edge locations), caching the data close where the user request
Global distributed Edge locations -> low latency + high scalability
CloudFront Signed URLs and Sign Cookies 🔗
Way to restrict content to specific users
With Signed urls, you can restrict download of a single file, with sign cookies you can allow multiple files.
Signed cookies only work with cloudfront, signed url work with both S3 and CloudFront
- A service creates a signed url or a signed cookie
- Users request to cloud front a file.
- CloudFront validates the signature, and give the data
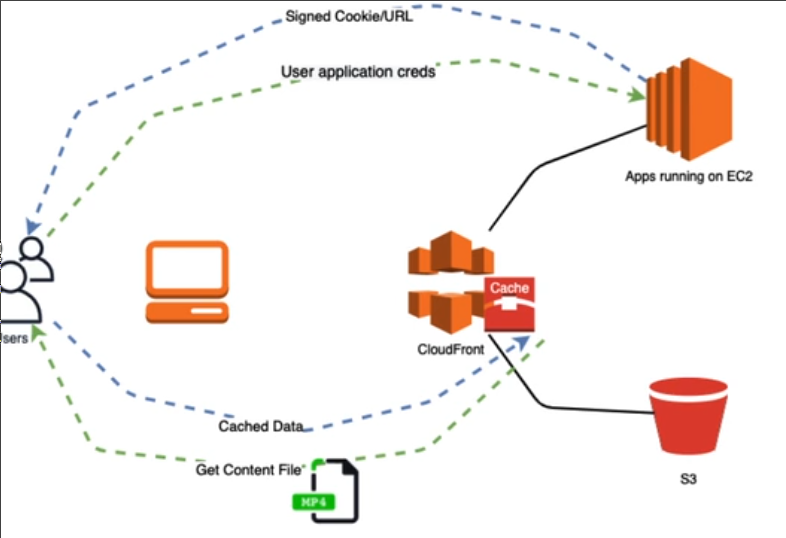
Restrict by:
- End date where url become no longer valid
- IP address or range
- Date and time that the URL becomes valid
S3 - OAI (Origin Access Identity) 🔗
To ensure that S3 files are only downloaded from the Cloudfront and users don’t go directly to the S3 url
- Create a special CloudFront user called OAI
- You associate an OAI to the cloud frount distribution.
- Change permission on the S3 bucket or objects, to only be readable by this OAI
Route 53 🔗
What can you do:
- Register domain names
- route internet traffic to the resources in AWS
- check health of the resourcers
Concepts:
- Domain name => coscolla.net
- Top Level domain => in coscolla.net is the
.net - subdomain => maps.google.com are subdomain of google.com
- Name servers => servers that resolve domain names to IP
- Types of Records:
- A => domain name to IP
- CNAME => domain name, to another domain name
- Alias => only exist in AWS => domain name to resource in AWS
Simple routing policy 🔗
Routes domain names to EC2 or ELB or IP
You can have multiple values in the record (multiple EC2 instances)
Weighted Roting policy 🔗
You can weight the amount of traffic to each record
Latency based Routing policy 🔗
Routes the traffic to the region that has lowest latency
Geolocation Routing policy 🔗
You can manually say that people from USA go routed to X region, so this way you can control the location / policy
Remember to set a default record, for when the R53 cannot resolve where are the client, if not there will be no answer
Failover routing policy 🔗
routes the traffic to a resource as long as the resource is healthy, and fallback to another resource if the primary is not healthy
Multivalue answer routing policy 🔗
let you return multiple values (IP addresses) like the simple routing policy, but this time it also allow you to add health checks and only return the values that are healthy
Analytics 🔗
EMR (Elastic Map reduce) 🔗
EMR is a managed cluster platform that simplified running big data frameworks (spark, hadoop) on AWS
Athena 🔗
Query service for S3 (unstructured or structured) files using SQL, Serverless
-> you can use to query AWS service logs (VPC Logs, ALB logs etc..)
QuickSight 🔗
cloud scale business intelligence service to deliver easy to understand insights (dashboards etc…)
Amazon Redshift 🔗
Managed petabyte scale data warehouse service in the cloud. Designed for OLAP and BI appls
-> The leader node makes a plan (compiled code) and each computer node executes part of the plan (Similar on how you do it in spark) -> The leader node caches some of the results -> There is a priroty system Workload Management to ensure that long queries don’t stuck on quick queries
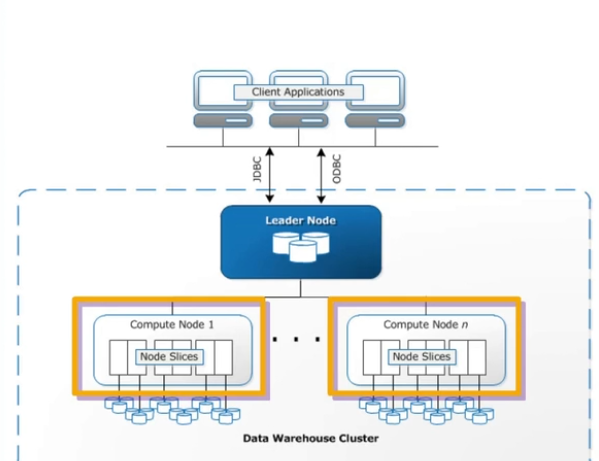
Redshift spectrum let the cluster of redshift to do complex analysis on objects stored AWS cloud (like S3 buckets)
- AQUA (Advanced Query Accelerator): low cost, easy to deploy, can boost query performance by 10x. IT resolves network bandwidth and memory processing bottleneck
Kinesis 🔗
Fully managed set of AWS services that allow to stream data to your applications. Realtime processing
Capabilities
- Kinesis Data streams: delivers data from producers to consumers (using shards)
- 1Mb per seconds per shard
- 1thousand records per second per shard
- max payload 1Mb
- Kinesis data firehose: from producers directly to destination (like an S3, redshift, ElasticSearch, Splunk, kinesis data analytics or custom http endpoint)
- You can add some transform configuring lambdas
- It has some buffers setting, so it’s almost realtime
- Kinesis analytics: allow you to do on the fly analytics and deliver to a destination
- Kinesis video streams: From producers of media (video, audio, camera)
Glue 🔗
Fully managed ETD service, transforming, clean, enriching data and moving data between data stores and data streams
- Glue data catalog: Persistent metadata store
- Crawler => connects to data store to determine the schema
- Glue ETL engine => generates python/scala code
- A flexible scheduler for dependency resolution (like Airflow?)
- is Serverless
Can be used to convert semi structured data to structured data (relational)
Integration 🔗
Step functions 🔗
Serveless orchestration service, to combina lambda functions and other AWS services to create flows
you build state machine, event driven workflow Each step is a state in the state machine
Two types of workflow:
- Standard workflow: at-most-once worflow execution (with retry)
- Express workflow: at least once workflow execution can run for up to 5min -> for streaming data procession or IoT data ingestion
Amazon MQ 🔗
Managed meessage broker service used to migrate an existing message broker to the cloud
- encrypt data at rest with Amazon managed, KMS managed or customer CMK
- suportes rabbitMQ and activeMQ
Difference with SNS+SQS => SNS+SQS is fully managed, you don’t need to manage 0 things. SNS+SQS should be used for new applications cause have more elastic scalability
SQS/SNS/SWF 🔗
SQS 🔗
Two types of consumer polling
- Short polling
- Long polling
Visibility timeout: after a consumer gets a message, how much time for this message to become visible again (0 sec, default: 15 sec, max: 12h)
Dead letter queues: a pool of messages that can’t be processed
Types of queues:
- Standard: Order can be messed up a little bit
- FIFO: order is conserved, and delivered exactly once
SNS 🔗
Pub / Sub
A producer publish an event, and the subscribers receive the event
Subscribers can be lambda, SQS, Http endpoint, email …
Fanout: When a single event has multiple subscribers (for example 2 SQS)
SWF (Simple workflow Service) 🔗
Similar to step functions (but processing can be on-promise)
Event Bridge 🔗
Serverless event buss to build event driven apps at scale
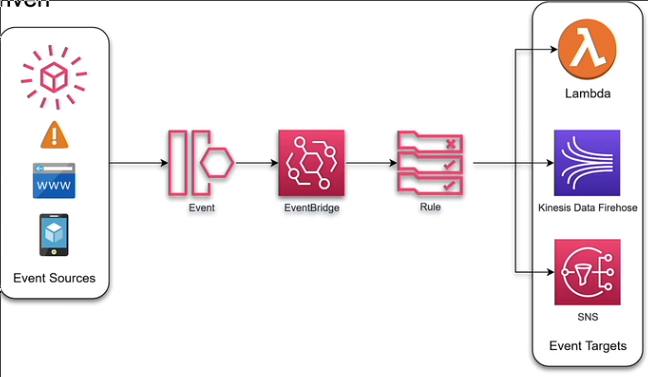
Use case:
- help rearchitect system using decoupled services
- Monitor your operations
You have 3 types of “bus”"
- default: you receive AWS events
- Custom: you receive events from other regions
- partner bus: from other SaaS apps
You can replay the events of the bus.
- Advance filtering
- Multiple destinations
Fargate 🔗
You can have ECS on EC2 instances or in Fargate (serveless infrastructure). So you only say how much resource each tasks need, and the cluster scales
EKS 🔗
Two components, the control panel and the worker nodes
Multiple AZ => HA
Replace unhealthy instances
Automated version updated and patching
nodes can be fargate or EC2
ECS is deployed in a VPC in 3 AZ
EKS vs ECS 🔗
- Effort (ECS easy), EKS is harder
- IAM (ECS you get), EKS (addon you need install and configure)
- Container limit => ECS (120), EKS (750)
- EKS can be multicloud
ECR 🔗
Container image repository in ECR, support for IAM
- Repository policy
- Lifecycle policies -> scan images, remove prior images (having max num of images)
- Cross region and cross acount replication
- you can use KMS to encrypt repository images
Migration & Transfer 🔗
DMS (Database Migration Service) 🔗
Help migrate and maintain data on premise database to another database. by parsing the logs of the database and moving them to another db.
AWS Data Sync 🔗
You install a AWS Data sync agent in yout premise data-center, and all changed done in a shared FS (SMB, NFS) can be replicated to the cloud (S3, FSx, EFS)
-> will use the internet connection, is recomended to have Direct connect (for the throughtput) or at least VPN
-> can be used (S3,EFS, Fsx) to (S3, EFS, Fsx) (between regions), in that case will not go to the public network
Migration Hub 🔗
A central location for discovering existing servers, plan server migrations, and track application migration status
Application Migration Service 🔗
can be used to migrate on-premise servers to AWS,
supports SAP, oracle, SQL Server migrations
AWS Server migration Service 🔗
uses snapshot-based replication which makes a cutover migration window in hours. Uses block level replication
Application discovery Service 🔗
collects data from existing servers at on premise which can be used by the client to understand server configurations, usage, behaviour etc…
- Agentless => you deploy a small VMWare hosts
- Agrent-based => for other hosts that are not VMWARE
Misc 🔗
AWS Config 🔗
- Can monitor the resources of an account -> not realtime
Proton 🔗
AWS Proton is a deployment workflow tooffl for modern applications that helps platform and DevOps engineers achieve organizational agility.
KeySpaces 🔗
Cassandra managed
WorkDocs 🔗
Secure document sharing and content collaborating
Control tower 🔗
Easy way to setup and goven a secure compliant multi-account AWS environment
Data Lifecycle Manage 🔗
You can use Amazon Data Lifecycle Manager to automate the creation, retention, and deletion of EBS snapshots and EBS-backed AMIs.
AWS Connect 🔗
Provide superior customer service at a lower cost with an easy-to-use omnichannel cloud contact center
AWS Outposts 🔗
Delivers AWS infrastructure and services to virtually any on-premises or edge location that provides a truly consisent hybrid experience.
Is like having your local AWS on premise, it literraly is a computer in format of U’s
ECS, EBS, EKS, EC2, S3, EMR,RDS, ALB….
You can connecto to VPC
Transfer Family 🔗
allow to transfer from/to AWS storage (EFS, S3) and SFTP, FTPS, FTP
AWS SSO 🔗
is like a Okta on AWS
- you can use your on-premise identity provider
- and you can add new appslications that support SSO
Polly 🔗
Service for TTS (text to speech)
- Custom lexicons => change pronunciation of certain words
- SSML => certain words to diferent style
- Newcaster Speaking Style => make it like spoken by a TV newcaster
- Brand Voice => allow customize the voice
Comprehend 🔗
managed NLP service, analize, understand and interpret meaning from a text
- can read data from S3
Lex 🔗
Fully managed AI service, to create conversational interface
Amazon Certificate Manager 🔗
support provisioning and managing SSL/TLS certificates to be used by amazon resources
- monitors expiration
- Certificates jmust be imported in US-EAST and used in any supported region
Tagging 🔗
Strategy 🔗
- Tagging by resource organization (ie. tag service of each resource)
- Cost allocation (be able to break down the cost by tags)
- Automation (we can query tags to know what to do in automated way)
- For access control -> IAM permissions can be done by tag condition